Méthodologie de création d'un
système Linux embarqué
La structure du système est calquée
sur les autres systèmes Unix libres ou propriétaires à savoir :
• un noyau ou kernel réalisant les
fonctions essentielles comme la gestion des tâches et de la mémoire, ainsi que
l’interfaçage entre le matériel et les applicatifs grâce entre autres aux pilotes de périphériques
ou en anglais device drivers ;
• une bibliothèque principale
appelée libc ou glibc (GNU libc) sous Linux et contenant
les fonctions de base utilisées par
les applicatifs ;
• les applicatifs eux-mêmes,
appelés également commandes, soit livrés en standard avec
le système ou bien développés pour
des besoins spécifiques.
À ces éléments standards il faut
ajouter un programme de démarrage ou bootstrap comme LILO (LInux LOader). À la
différence des autres composants du système, le programme de démarrage ou chargeur est
très dépendant du matériel utilisé.
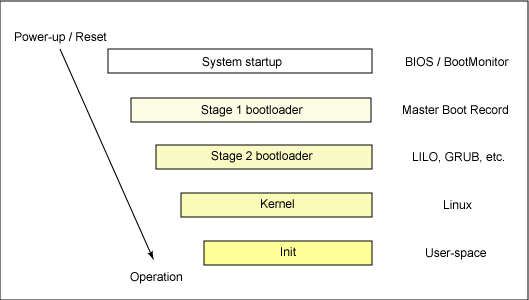
Le schéma de démarrage d’un
système Linux est relativement simple et on peut le décomposer comme suit :
1. Chargement du système par LILO ou
un programme équivalent, comme GRUB.
2. Chargement du noyau Linux. Le
chargement s’accompagne de l’initialisation des périphériques matériels
indispensables au démarrage, et donc au chargement des pilotes de
périphériques associés. Le noyau Linux tente également de charger
sa partition principale ou root partition sur
laquelle il ira chercher les éléments nécessaires à la suite du lancement du système.
3. Lorsque le noyau Linux est chargé,
il exécute un programme d’initialisation qui, par défaut, correspond à la commande
/sbin/init. Cependant, on peut indiquer facilement au noyau de passer la main à un
autre programme.
4. Dans le cas de l’utilisation du
programme init standard, ce dernier explore le fichier de configuration /etc/inittab qui
contient le chemin d’accès à un script de démarrage, comme ceci :
# System
initialization (runs when system boots).
si:S:sysinit:/etc/rc.d/rc.d/rc.sysinit
Le script en question poursuit
l’initialisation du système.
1.Le noyau LINUX
Le noyau est l’élément principal
du système, d'abord parce que ce noyau fut initialement conçu par
Linus Torvalds, créateur du système Linux et de composants
provenant en majorité du projet GNU de Richard Stallman. Ensuite
parce que la structure monolithique du noyau en fait l’interface
unique entre le système et le matériel dans la
quasi-totalité des cas de figure.
1.1. Structure globale du noyau
Dans le cas de Linux, le noyau est un
fichier exécutable, monolithique ou presque, chargé d’assurer les fonctions
essentielles du système comme la gestion des tâches, ou scheduling,
la gestion de la mémoire et le pilotage des périphériques que
ceux-ci soient réellement des périphériques matériels ou bien
qu’ils soient des périphériques virtuels.
Dans une distribution Linux
classique, le noyau est physiquement représenté par un fichier localisé sur le répertoire
/boot :
serge@serge-Aspire-4830TG:/boot$
ls -lrt
total
46484
-rw-------
1 root root 2320733 Oct 9 2012 System.map-3.5.0-17-generic
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 154429 Oct 9 2012 config-3.5.0-17-generic
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 853738 Oct 9 2012 abi-3.5.0-17-generic
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 5171760 Oct 17 19:08 vmlinuz-3.5.0-17-generic
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 178944 Jan 3 23:47 memtest86+_multiboot.bin
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 176764 Jan 3 23:47 memtest86+.bin
-rw-------
1 root root 5169520 Mar 25 21:29 vmlinuz-3.5.0-27-generic
-rw-------
1 root root 2320304 Mar 25 21:29 System.map-3.5.0-27-generic
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 154652 Mar 25 21:29 config-3.5.0-27-generic
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 860818 Mar 25 21:29 abi-3.5.0-27-generic
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 15066322 Apr 16 21:16 initrd.img-3.5.0-17-generic
drwxr-xr-x
5 root root 4096 Apr 16 21:29 grub
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 15142645 Apr 16 21:30 initrd.img-3.5.0-27-generic
Le
nom du noyau est libre mais il est généralement suffixé en
fonction de la version du noyau,
ici 3.5.0 et de
l’extra-version choisie par celui qui a généré ce noyau, soit 17
dans le
cas présent.
Nous
verrons que l’extra-version est définie dans le fichier Makefile
de l’arborescence des sources du noyau.
Le
noyau Linux utilise également un fichier nommé System.map
qui contient des informations sur des adresses internes du noyau. Ces
informations sont utiles à la gestion des modules décrits ci-après. Le fichier System.map est également
présent sur le répertoire /boot. En toute rigueur, il est lié à la version complète
du noyau généré, y compris l’extra-version, car il est généré lors de la compilation du
noyau.
1.2. Les modules chargeables du
noyau
Dans les cas d’applications
classiques de Linux, le noyau utilise le plus souvent des modules qui peuvent être
dynamiquement chargés et déchargés en fonction des besoins du système.
Ces modules peuvent être des pilotes
de périphériques matériels, comme des cartes d’extension, ou
bien liés à un support générique de plus haut niveau comme le
support SCSI. L’utilisation des modules permet d’optimiser la
mémoire du système à un instant donné car un pilote non utilisé
pourra être déchargé, libérant ainsi sa mémoire.
De même, l’utilisation des modules
permettra d’ajouter dynamiquement des périphériques sans redémarrer le système.
Dans le cas d’un noyau embarqué,
on pourra cependant se poser la question quant à l’utilisation des
modules sachant que ceux-ci nécessitent la validation d’options
spécifiques lors de la compilation du noyau, ce qui augmente
légèrement sa taille. De même, la hiérarchie des modules
nécessite la mise en place du répertoire /lib/modules, ce qui
augmente le nombre de fichiers, la complexité du système et aussi
légèrement l’espace occupé par ce dernier.
Le choix de l’utilisation ou non
des modules sera laissé à la charge de l’intégrateur du système en fonction de ses besoins.
serge@serge-Aspire-4830TG:/boot$
ls -l /lib/modules
total
8
drwxr-xr-x
4 root root 4096 Oct 17 17:00 3.5.0-17-generic
drwxr-xr-x
4 root root 4096 Apr 16 21:28 3.5.0-27-generic
À
chaque sous-répertoire correspond une version du noyau. Dans le cas
présent, les
modules
utilisés par le noyau seront localisés dans le répertoire
3.5.0-17.
serge@serge-Aspire-4830TG:/lib/modules$
ls -l 3.5.0-17-generic
total
4640
lrwxrwxrwx
1 root root 39 Nov 14 23:08 build ->
/usr/src/linux-headers-3.5.0-17-generic
drwxr-xr-x
2 root root 4096 Oct 17 16:58 initrd
drwxr-xr-x
10 root root 4096 Oct 17 16:59 kernel
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 739381 Oct 17 17:00 modules.alias
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 719847 Oct 17 17:00 modules.alias.bin
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 6027 Oct 9 2012 modules.builtin
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 7365 Oct 17 17:00 modules.builtin.bin
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 69 Oct 17 17:00 modules.ccwmap
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 351471 Oct 17 17:00 modules.dep
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 518442 Oct 17 17:00 modules.dep.bin
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 214 Oct 17 17:00 modules.devname
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 889 Oct 17 17:00 modules.ieee1394map
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 295 Oct 17 17:00 modules.inputmap
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 21817 Oct 17 17:00 modules.isapnpmap
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 2486 Oct 17 17:00 modules.ofmap
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 144391 Oct 9 2012 modules.order
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 471479 Oct 17 17:00 modules.pcimap
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 1765 Oct 17 17:00 modules.seriomap
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 131 Oct 17 17:00 modules.softdep
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 285690 Oct 17 17:00 modules.symbols
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 363056 Oct 17 17:00 modules.symbols.bin
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 1063926 Oct 17 17:00 modules.usbmap
Les
modules sont répartis dans des sous-répertoires selon une
classification fonctionnelle.
La
liste ci-après permet de visualiser les modules correspondant à des
pilotes réseau :
serge@serge-Aspire-4830TG:/lib/modules/3.5.0-17-generic$
ls -l /lib/modules/3.5.0-17-generic/kernel/drivers/net | head
total
244
drwxr-xr-x
2 root root 4096 Oct 17 16:59 appletalk
drwxr-xr-x
2 root root 4096 Oct 17 16:59 arcnet
drwxr-xr-x
2 root root 4096 Oct 17 16:58 bonding
drwxr-xr-x
2 root root 4096 Oct 17 16:59 caif
drwxr-xr-x
7 root root 4096 Oct 17 16:59 can
drwxr-xr-x
2 root root 4096 Oct 17 16:59 dsa
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 7464 Oct 9 2012 dummy.ko
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 9280 Oct 9 2012 eql.ko
drwxr-xr-x
46 root root 4096 Oct 17 16:59 ethernet
serge@serge-Aspire-4830TG:/lib/modules/3.5.0-17-generic/kernel/net/wireless$
ls -lrt
total
268
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 9608 Oct 9 2012 lib80211.ko
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 6760 Oct 9 2012 lib80211_crypt_wep.ko
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 12672 Oct 9 2012 lib80211_crypt_tkip.ko
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 8328 Oct 9 2012 lib80211_crypt_ccmp.ko
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 225020 Oct 9 2012 cfg80211.ko
Le
fichier modules.dep contient les dépendances entre les
modules sous la forme d’une
simple
liste contenant une définition de dépendance par ligne. Cette liste
est générée au
démarrage
du système par la commande depmod
-a.
On
doit également utiliser cette commande chaque fois que l’on ajoute
un nouveau
module
à l’arborescence des modules. Un extrait de la liste est présenté
ci-après :
/lib/modules/2.4.7-10/kernel/fs/vfat/vfat.o:
/lib/modules/2.4.7-10/kernel/fs/fat/fat.o
La
ligne ci-après montre que le module vfat.o nécessite la
présence du module fat.o.
Bien
que les modules soient normalement chargés de manière automatique
par le système, nous allons décrire en quelques lignes les
principales commandes de manipulation des
modules, et ce afin de donner un bon aperçu des opérations
possibles sur les modules.
Remarque
Les
modules sont manipulés grâce à un paquetage nommé modutils.
En cas d’utilisation du noyau 2.6, il est nécessaire
d’utiliser une version récente du paquetage (module-init-tools-3.0
ou supérieur) disponible en téléchargement avec les sources du
noyau. Ces dernières versions sont compatibles 2.4 et 2.6.
On peut forcer le chargement d’un module en utilisant la commande insmod. Prenons l’exemple d’un module hello.o sans dépendance avec aucun autre module.
On peut charger ce module au moyen de la commande :
root#> insmod hello.o
On peut aussi ajouter ce module à l’arborescence des modules standards en effectuant :
root#> cp hello.o /lib/modules/2.4.7-10/kernel/drivers/char/lib/modules/2.4.7-1/kernel/driver/char
root#> depmod -a
puis charger ce module avec la commande :
root#> insmod hello Using /lib/modules/2.4.7-10/kernel/drivers/char/hello.o
Notez qu’il est nécessaire d’être super-utilisateur pour charger un module.
Dans le cas où le module est installé dans l’arborescence, on ne spécifie pas le suffixe. La trace du chargement effectif du module est visible dans le fichier des messages du noyau(dmesg). On peut également vérifier sa présence en utilisant la commande lsmod:
root#> dmesg | tail -1
Hello world!
root#> lsmod
Module Size Used by
hello 292 0 (unused)
Lors du chargement du module, il est possible de spécifier des paramètres par la ligne de commande :
root#> insmod bttv card=39
Les paramètres peuvent être spécifiés dans le fichier /etc/modules.conf afin d’être utilisés automatiquement lors du chargement du module. Dans le cas du noyau 2-6, on utilise le fichier /etc/conf.modules :
alias eth0 3c59x
options i2c-algo-bit bit_test=1
options bttv card=39
La commande alias permet de faire une association automatique entre un nom de module générique et le nom de module effectif. Dans le cas présent, le module 3c59x sera chargé lors de l’initialisation de l’interface réseau Ethernet qui nécessite le module générique eth0. Après chaque modification du fichier, on doit utiliser la commande /sbin/depmod -a.
Pour décharger le module, on utilise la commande rmmod :
root#> rmmod hello
root#> dmesg | tail -1
Goodbye cruel world!
Remarque
Dans le cas de modules dépendant d’autres modules, on ne peut cependant pas utiliser la commande
insmod.
Le système de fichier /proc
Pour communiquer avec l’espace utilisateur, le noyau Linux utilise un concept emprunté à Unix System V : le système de fichier /proc. À la différence des systèmes de fichiers classiques qui sont associés à des périphériques réels, le système de fichier /proc est virtuel. Sa structure de système de fichier en fait une représentation facile pour manipuler des paramètres du noyau Linux. On peut en effet utiliser les commandes standards de manipulation des fichiers classiques, ainsi que la redirection des entrées/sorties très utilisée sous Linux.
On peut aussi:
lister les modules charger dans le kernel:
root#> cat /proc/modules
visualiser la mémoire disponible:
root#> cat /proc/meminfo
visualiser les systèmes de fichiers supportés par le noyau:
root#> cat /proc/filesystems
visualiser la version du noyau:
root#> cat /proc/version
visualiser le type de processeur utilisé:
root#> cat /proc/cpuinfo
De même, les valeurs numériques présentes dans /proc représentent les zones d’information des processus courant, chaque valeur correspondant au PID du processus en question. Ces sous-répertoires contiennent les informations propres au processus en question :
serge@serge-Aspire-4830TG:/proc$ ls -l /proc/3962
ls: cannot read symbolic link /proc/3962/cwd: Permission denied
ls: cannot read symbolic link /proc/3962/root: Permission denied
ls: cannot read symbolic link /proc/3962/exe: Permission denied
total 0
dr-xr-xr-x 2 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 attr
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 autogroup
-r-------- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 auxv
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 cgroup
--w------- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 clear_refs
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 cmdline
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 comm
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 coredump_filter
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 cpuset
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 cwd
-r-------- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 environ
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 exe
dr-x------ 2 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 fd
dr-x------ 2 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 fdinfo
-r-------- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 io
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 latency
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 limits
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 loginuid
dr-x------ 2 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 map_files
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 maps
-rw------- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 mem
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 mountinfo
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 mounts
-r-------- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 mountstats
dr-xr-xr-x 5 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 net
dr-x--x--x 2 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 ns
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 oom_adj
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 oom_score
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 oom_score_adj
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 pagemap
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 personality
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 root
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 sched
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 schedstat
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 sessionid
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 smaps
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 stack
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 stat
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 statm
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 status
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 syscall
dr-xr-xr-x 3 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 task
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 20 13:36 wchan
Par exemple, le fichier status contient des informations sur l’état du processus en question.
Le système de fichier /proc est également utilisable en écriture, ce qui permet de
modifier dynamiquement le comportement du noyau Linux sans aucune compilation.
Un exemple classique est la validation d’option comme par le transfert de paquets IP (IP forwarding). On peut connaître la valeur de l’option d’IP forwarding en faisant :
root#> cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
1
Le système retourne la valeur 1, ce qui signifie que l’IP forwarding est validé. On peut l’inhiber en faisant simplement :
root#> echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
Une description complète du pseudo-système de fichiers
/proc est disponible dans le répertoire de documentation des sources du noyau Linux, soit :
root#> more usr/src/linux-2.4/Documentation/filesystems/proc.txt
pour les noyaux 2.4 et 2.6.
###########################################################
Bibliographie
- Linux embarqué (2e edition - Eyrolles)
- wikipédia